 In the realm of design operation, success hinges on scrupulous planning. A well-drafted design plan serves as the roadmap, guiding the platoon through colorful phases of the design lifecycle. From commencement to completion, each step is precisely orchestrated to ensure effectiveness and effectiveness. Then are 10 essential rudiments that form the backbone of a successful design plan
In the realm of design operation, success hinges on scrupulous planning. A well-drafted design plan serves as the roadmap, guiding the platoon through colorful phases of the design lifecycle. From commencement to completion, each step is precisely orchestrated to ensure effectiveness and effectiveness. Then are 10 essential rudiments that form the backbone of a successful design plan
- Clear objects: The foundation of any design plan lies in easily defined objects. These objects serve as the north star, guiding every decision and action throughout the design. They should be specific, measurable, attainable, applicable, and time-bound (SMART), furnishing a clear understanding of what needs to be fulfilled.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
- Comprehensive Scope Statement: A detailed compass statement outlines the boundaries of the design, including deliverables, constraints, and hypotheticals. It helps compass creep by easily defining what’s and is not included in the design, ensuring that the platoon stays concentrated on the primary pretensions.
- Stakeholder Identification and Engagement: Relating stakeholders and understanding their prospects is pivotal for design success. A successful design plan involves engaging stakeholders beforehand and frequently, soliciting their input, and managing their prospects throughout the design lifecycle.
- Resource Allocation: Effective resource operation is essential for optimizing design issues. This includes allocating mortal, fiscal, and material coffers in a way that maximizes effectiveness and minimizes waste. A well-defined resource plan ensures that the necessary coffers are available when demanded.
- Detailed Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Breaking down the design into manageable tasks is crucial to successful prosecution. A WBS organizes the work into lower, more manageable factors, making it easier to assign liabilities, estimate time and costs, and track progress.

- Realistic Schedule: Developing a realistic schedule is critical for meeting design deadlines and mileposts. A well-allowed-out design plan includes a timeline that accounts for dependencies, pitfalls, and contingencies, allowing for adaptations as demanded to keep the design on track.
- Risk Management: Plan Every design comes with essential pitfalls, and effective threat operation is essential for mollifying implicit pitfalls. A comprehensive threat operation plan identifies, assesses, and prioritizes pitfalls, as well as outlines strategies for managing or mollifying them throughout the design lifecycle.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
- Communication Plan: Open and effective communication is vital for design success. A communication plan defines who needs to communicate, what information needs to be collected, and how and when communication will be done. It ensures that all stakeholders are kept informed and engaged throughout the design.
- Quality Management Plan: Delivering a high-quality end product is a primary ideal of any design. A quality operation plan outlines the norms and processes for ensuring that deliverables meet the specified conditions and prospects. It includes quality assurance measures to help blights and quality control measures to identify and correct any issues that arise.
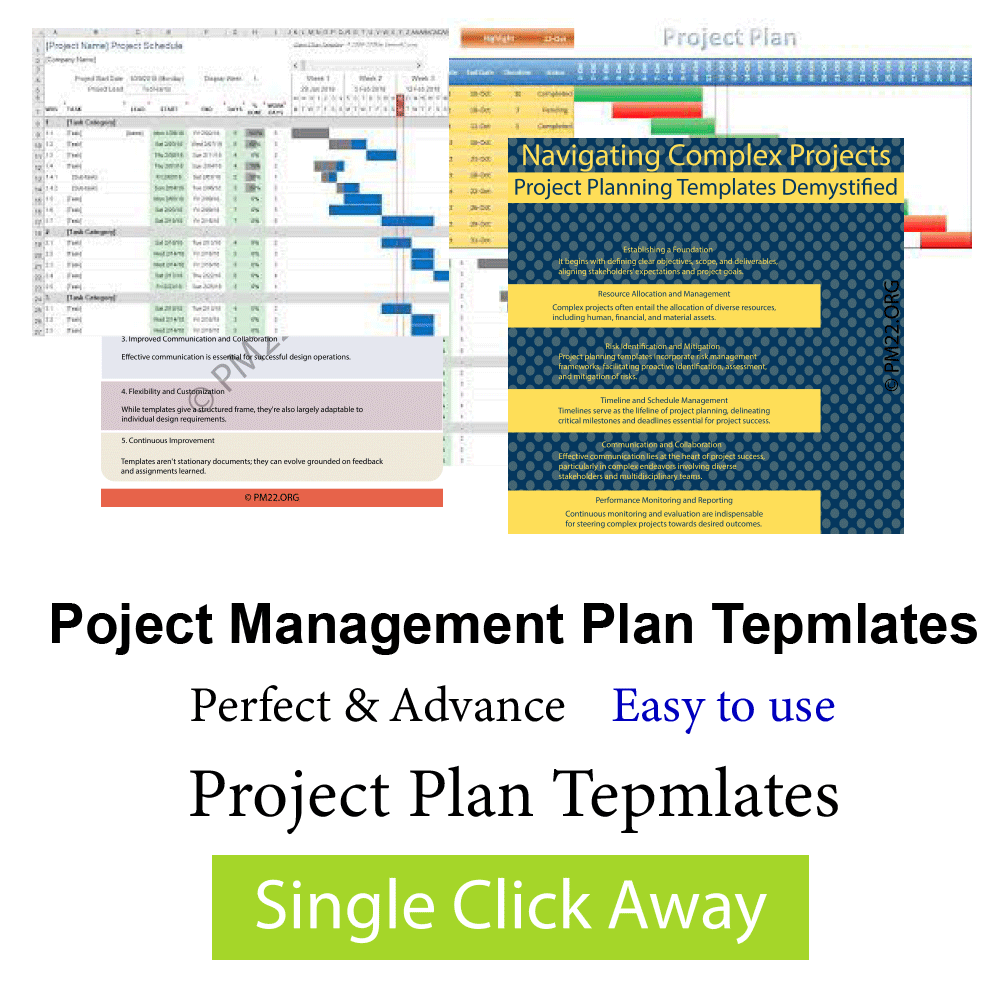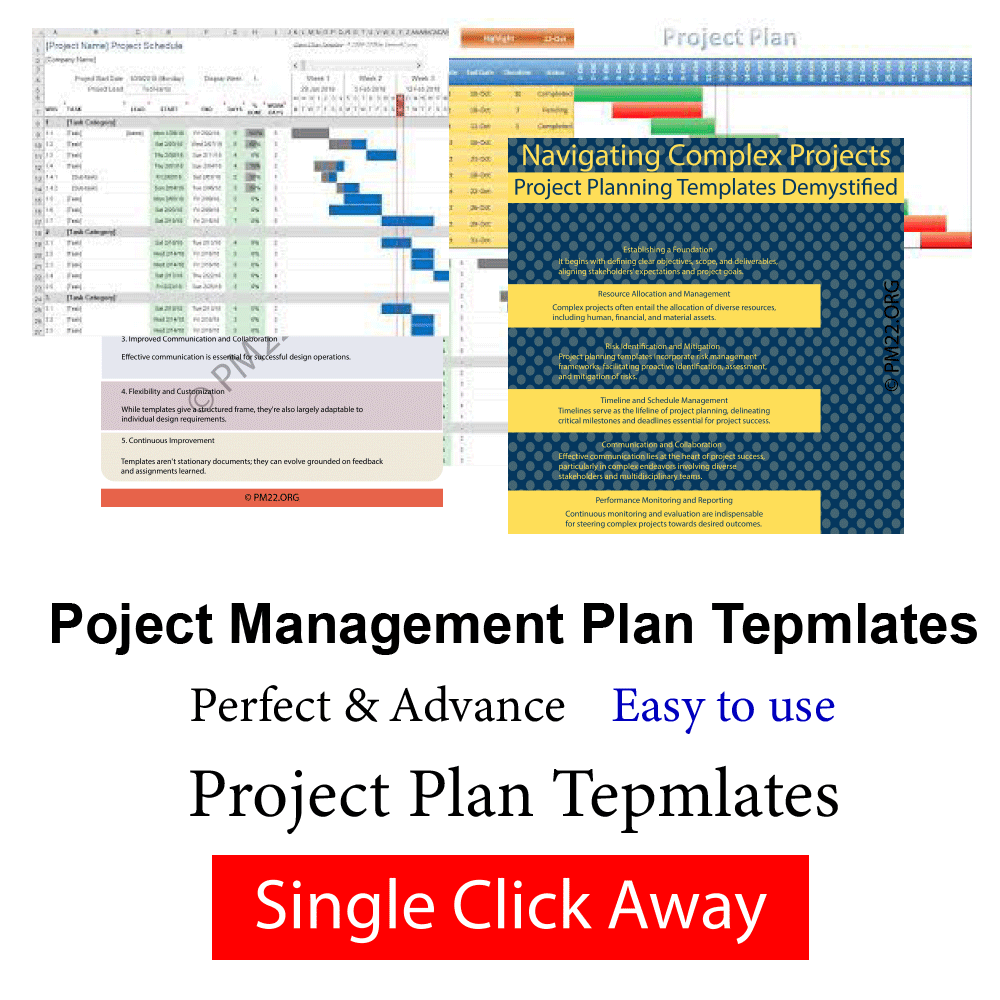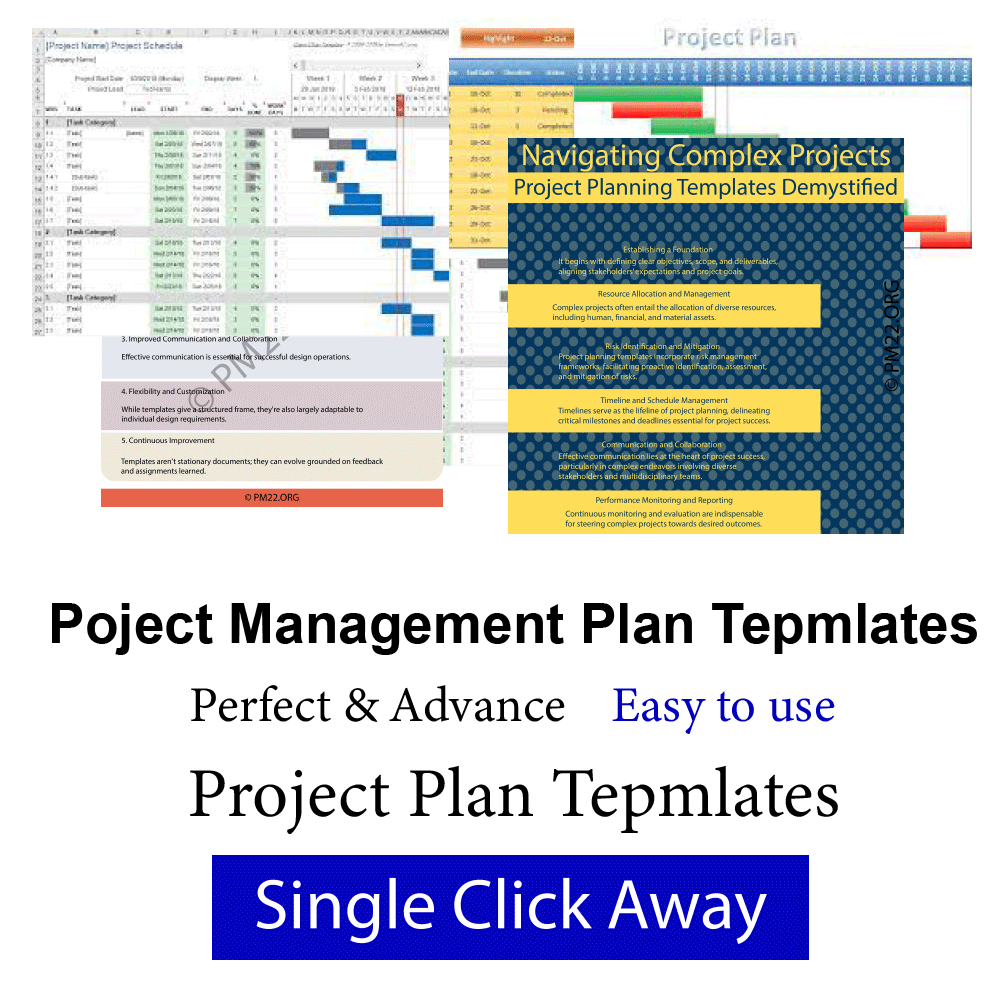
- Monitoring and Control Mechanisms: Monitoring progress and controlling changes are essential for keeping the design on track. A successful design plan includes mechanisms for tracking progress, measuring performance against objects, and relating diversions from the plan. It also establishes procedures for managing changes and making adaptations as necessary to maintain design quality and delivery.
In conclusion, a successful design plan is the capstone of careful planning, collaboration, and prosecution. By incorporating these 10 essential rudiments into their design plans, design directors can increase the liability of achieving their pretensions and delivering successful issues. From setting clear objects to enforcing robust monitoring and control mechanisms, each element plays a critical part in icing design success.
