 Effective Design planning is the foundation of successful prosecution. Whether you are managing a small platoon or leading a large-scale action, the capability to plan strictly can make the difference between smooth sailing and chaotic turbulence. Learning the art of design planning requires a combination of foresight, attention to detail, and strategic thinking. In this composition, we’ll explore the crucial rudiments of design planning and give practicable keenness to help you confidently navigate any design’s complications.
Effective Design planning is the foundation of successful prosecution. Whether you are managing a small platoon or leading a large-scale action, the capability to plan strictly can make the difference between smooth sailing and chaotic turbulence. Learning the art of design planning requires a combination of foresight, attention to detail, and strategic thinking. In this composition, we’ll explore the crucial rudiments of design planning and give practicable keenness to help you confidently navigate any design’s complications.
- Define Clear objects: Before diving into the nitty-gritty of planning, it’s essential to define clear and attainable objects for your design. What are you aiming to negotiate? What are the issues asked? Establishing clear objects serves as a guiding light throughout the planning process, helping you stay focused and aligned with the design’s purpose.
- Understand Stakeholder: Needs Identify and engage with crucial stakeholders to understand their requirements, prospects, and enterprises. Stakeholder input is inestimable for shaping design pretensions, relating implicit pitfalls, and icing alignment with organizational precedence. By laboriously involving stakeholders from the onset, you can foster a sense of power and collaboration that enhances design success.
- Develop a Comprehensive: Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Break down the design compass into manageable tasks and subtasks, creating a hierarchical structure known as the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). This step-by-step corruption allows you to fantasize about the design’s factors, allocate coffers effectively, and establish clear responsibility for each deliverable.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
- Estimate Time and coffers: Accurate estimation of time, budget, and coffers is critical for realistic planning and scheduling. Use literal data, expert judgment, and design operation tools to estimate the duration and trouble needed for each task. Factor in implicit pitfalls and misgivings about contingencies and buffer time.
- Produce a Realistic Schedule: Develop a design schedule that outlines the sequence of conditioning, dependencies, and mileposts from launch to finish. Use Gantt maps, network plates, or other scheduling ways to fantasize the design timeline and identify critical paths. Be realistic about timelines, considering resource constraints, dependencies, and implicit backups.
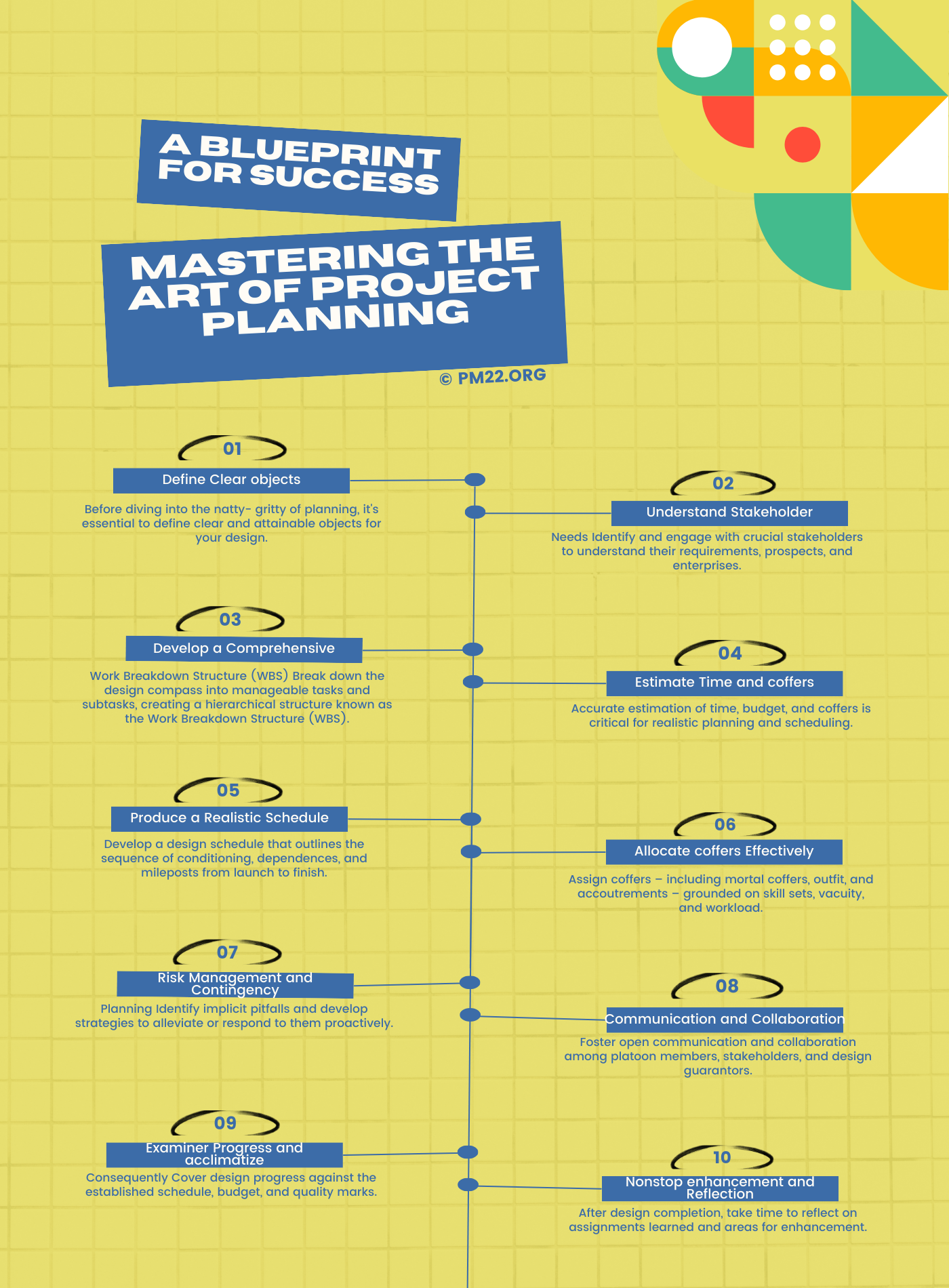
- Allocate coffers Effectively: Assign coffers – including mortal coffers, outfits, and accouterments – grounded on skill sets, vacuity, and workload. Balance workloads to help collapse and optimize productivity. Regularly review resource allocation throughout the design lifecycle to acclimate to changing conditions and precedences.
- Risk Management and Contingency: Planning Identify implicit pitfalls and develop strategies to alleviate or respond to them proactively. Conduct threat assessments to assess the viability and impact of colorful pitfalls, similar to compass creep, resource constraints, or external dependencies. Establish contingency plans and indispensable courses of action to minimize dislocations and keep the design on track.
- Communication and Collaboration: Foster open communication and collaboration among platoon members, stakeholders, and design guarantors. Establish clear channels for participating updates, progress reports, and feedback. Regularly communicate design status, mileposts, and challenges to keep stakeholders informed and engaged.
- Examiner Progress and Acclimatize: Consequently, Cover design progress against the established schedule, budget, and quality marks. Use design operation tools and performance criteria to track crucial pointers and identify diversions from the plan. Be set to acclimatize and acclimate course as demanded, responding to changing conditions, stakeholder feedback, or unlooked-for circumstances.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
- Nonstop enhancement and Reflection: After design completion, take time to reflect on assignments learned and areas for enhancement. Conduct posthumous reviews to dissect successes, challenges, and openings for improvement. Incorporate feedback into unborn design planning sweats to continuously upgrade and optimize your approach.
In conclusion, learning the art of design planning is a dynamic process that requires industriousness, foresight, and rigidity. By defining clear objectives, engaging stakeholders, developing a comprehensive plan, and embracing visionary threat operations, you can navigate the complications of any design with confidence and achieve success. Flashback, effective planning lays the foundation for successful prosecution, enabling you to deliver results that exceed prospects and drive meaningful impact.
