Agile is an advanced project management method that is used to run projects well. It is especially helpful for software development projects. It is different from traditional project management techniques. The more common something is, the more details it has, the more it is based on features, and the more the team owns it.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
Usually, project plans are made up of a list of tasks, how long each task will take, and how it will affect other tasks. Most of the time, these plans are based on the assumptions that project managers and project teams have made. But these plans predict everything about the activities, how long they will last, and who is in charge.
Agile Project Plan
An agile project plan is based on a method that looks at iterations or sprints to see how much work they can get done.
Agile planning tells us which project tasks are done in each sprint and helps us come up with a method that can be used again and again to finish a task. This method saves cost and time, and other working staff can get advice on how to finish a project task.
On the other hand, the agile project plan template helps project managers decide how to proceed forward based on the features of the project. Its key focus is on the delivery of features and the iterative information approach.
In an agile approach, assumptions are made in such a way that we don’t know anything about the situation after a certain amount of time.
Depending on how important the features are, though, a good guess can be made about when they will be delivered. The time frame is also estimated based on how well the project team works.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
Pros and Cons of an Agile Project Plan
The way agile projects are planned is very different from the way projects have been managed in the past. A few of the most fundamental differences are;
Based on the project’s features, the agile project plan outlines the activities, how long they will take, and how they will affect each other. Also, it makes assumptions based on features, whereas the traditional system relied on the knowledge of project managers and project teams to make all of its assumptions.
Second, the agile project plan gives a lot of information about a short amount of time, like 2 to 4 weeks, so that the project team can guess what will happen. During the whole project’s lifecycle, this iteration is done several times.
In agile project management, the work done during this iteration period is based on the prioritisation of features and the functional ability of the project team, which is called velocity. Things change over time, and so do priorities and the project team.
In traditional project management, project managers and teams, on the other approach, use all of the available resources right away. In the planning stage, make a detailed plan for the project that looks ahead to all possible events and risks.
Elements of a Template for an Agile Project Plan
The agile project plan template is made up of four essential components.
The agile project plan template is based on releases and sprints. The release explains how new products will be made and how old ones will be improved. The iterations of each release that are changed are called sprints. For a short period of time, these sprints are based on user stories that give detailed information about the work.
The project managers and team are in charge of the user stories. The project team has a list of tasks that have been assigned. It gives project managers an overview of how things are going and lets them know when there are issues.
The iterative and incremental nature of the agile project plan is its most key trait. All sprints have the same length and are done in the same way. This process helps the team learn about their speed, what slows them down, and what they can do.
It encourages the project team to be involved in the planning and estimating phase of the project.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
Excel Template for Phases of an Agile Project Plan
Here are the seven phases of planning in an agile way;
- Getting a clear identification of the agile product vision
- Making a plan for an agile product roadmap
- The Agile Release Plan was made.
- How to Make a Plan for Agile Sprints
- Schedule Agile Scrum meetings every day.
- Review of Agile Iterations
- Retrospective on Agile Iterations
The only thing we do in the first phase of agile planning is figure out the product’s vision and scope. In the second phase, the planning, roadmap, and structure of the work plan are made. We release the agile plan after making a specific roadmap for the agile product.
Now, we make agile iteration plans, which are called sprints. In the 5th phase of agile planning, we met with the Scrum Master to talk about how to make these sprints better.
These iterations also need to be based at from a user’s point of review. Basically, this is where we get feedback from people who are working on this process and evaluate risks and problems that need to be fixed.
This agile product production plan’s seventh and final phase is based on recycling the process if everything in this plan is working right.

CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
Plan for a SAP Agile project
But a typical SAP project has a full list of tasks, a timeline with start and end dates, details about RACI, a list of priorities for deliverables, and instructions. Now it’s time to break this plan up into 6 phases called “sprints.” Each sprint has its own way of getting things done.
Change management, data migration, designing and developing, and project infrastructure impact analysis results were all a development of these sprints.
Change Management
This phase is needed for any new system that changes in a direct or indirect change. We all know that people don’t like change, but here we make changes by dealing with user conflicts. So, we set up Standard Operating Procedures to help users adapt to change and keep problems from happening.
Data Migration
After the new system is set up, it’s time to move the data to it. Because we need all the data from the old system. Part of this phase is also writing the coding for SAP modules.
Designing and Development
During this phase, the project’s road map is made. Basically, this is where we make a new project work timeline for the new system. Then, we run the same tests on this new system that we ran on a different system with the same specs.
Infrastructure
In this phase, you buy the equipment and other resources you need to set up the conditions for running tests. As part of this phase, security measures are also put in place.
Impact Analysis
This is the most important part of making a new system. It helps figure out what it needs and how it works. This also helps solve problems that might come up during the process of switching to a new system.
Plan for Scheduling an Agile Project
Here, we talk about the complete process of planning an Agile project schedule, which will help you make an agile project plan. This agile schedule plan has 8 steps, which are as follows:
A discussion about NEEDS
This first step talks about the goals, the steps that need to be taken to make the product easy to use, and what the customer wants and needs.
Detailing
In this step, we focus on product features and factors, dependencies, manufacturing requirements, and other risk factors that can affect the product delivery process. But it’s best to plan the features that are high-risk but have a lot of value.
Needs Work on Planning
This step is important because it depends on the morale of the team and how quickly work got done in previous sprints. Every sprint, we can join a team. But don’t forget the current work hierarchy, problems, and resources.
Stories, Epics, and Initiatives
- Stories: These are the few requirements that have been planned to meet the requirements of the end user.
- Epics: This is a work for big jobs that are broken up into smaller tasks.
- Initiatives: Writing all the epics that have the same goals.
Iteration
It means work and tasks that are planned and done for a limited period of time. There are due dates for all tasks and work that must be met. Iterations are like the building blocks for Agile development in a SAF structure.
Adding Stories in iteration
We need to add user stories so that it can work at a high level.
Putting in more loops
You need more iterations to cover all user stories or to get past user stories that aren’t as extra. This step helps you figure out when the product will come out.
Plan Sharing
In the last step, we tell our team members, clients, customers, and other important stakeholders about our plan and ask for their feedback, suggestions, etc.
Agile Project Plan: Sprint Planning Process
Here is another process for planning that defines the plan for a new Sprint for an Agile team. Here are the next eight steps:
Old Minutes of Meetings
In this step, we hold a meeting to talk about the old sprints’ plans, results, and lessons learned. This helps break the momentum.
Having a Sprint plan Meeting
From this meeting, we analyse and get information that helps us make a product release plan and updates on the previous sprint, any changes that need to be made, adding new features, etc.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
User Stories Detailing
Always pay attention to the details in User stories that help make plans or tasks better and more in line with what users want.
Divide User Stories into Tasks
Now it’s time to separate the user stories into small tasks.
Assigning Tasks
Now that you’ve made tasks, you can give them to team members and set rules and RACI.
Write the tasks down.
Scrum master writes the list of tasks on a big whiteboard where everyone on the team can see them. But the user stories in the current sprint are the most recent ones and must be at the top of the list.
Tracking Task Progress
Now it’s time to keep track of how the task is going. The scrum master will get a daily task report from each team member. Or change any template for keeping tracking of progress. After that, the scrum master will analyse at how the task was completed, whether it was done correctly, on time, or not at all.
Tracking track with the Burndown Chart
A Burndown chart helps show how much time and resources have been used and how much is left, as well as the status of a task, whether it is behind or ahead of schedule, etc.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
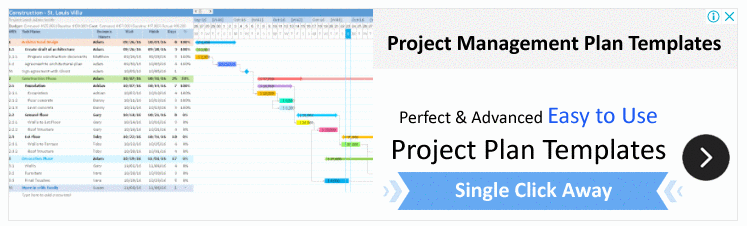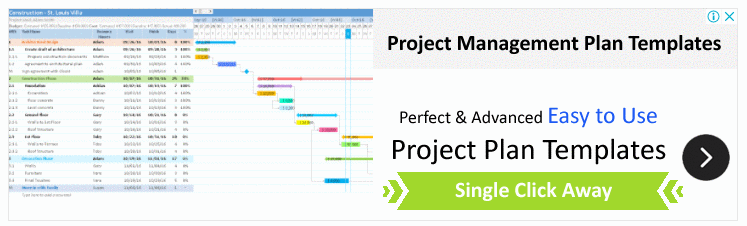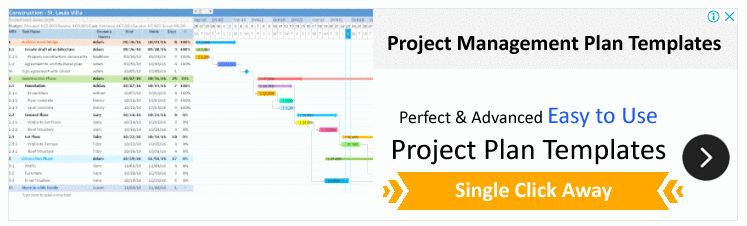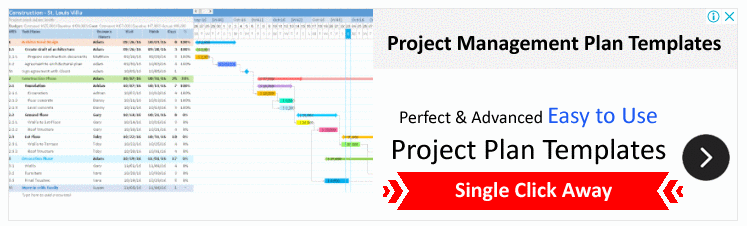
Creating an Agile Project Plan in Excel Template
It’s easy to use an Agile Excel project plan template in which you can put your project plan data and track progress. Although, its Excel template made a Gantt chart that was based on your Agile project plan.
Here are a few details you need to add to the excel datasheet:
- Project Name: Here, you must give a specific name or an identification number.
- Sprint: Sprints should go here.
- Tasks: This is where you can add a list of tasks, along with their details, subtasks, and upcoming milestones.
- Responsible: Set someone in charge of doing this job.
- Start Date: You have to say when the tasks will begin.
- Date to end: When the task is done Date here.
- Progress: Here you can share project timeline details.
- Status: In this section, you can talk about the status of a task or what has happened recently.
- Time: Start Date is on the horizontal axis and End Date is in the columns.
- Tasks: On the Vertical Axis, project tasks, milestones, and project phases can be shown.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL