 Portfolio management in project settings is the key to balancing resources, aligning projects with strategic goals, and driving long-term success. While project management focuses on individual projects, portfolio management looks at the bigger picture—ensuring that the entire portfolio of projects delivers value to the organization. Planning for portfolio management is not a one-size-fits-all process, but there are core principles you can follow to lay a strong foundation. Let’s dive into a practical approach to planning for effective portfolio management.
Portfolio management in project settings is the key to balancing resources, aligning projects with strategic goals, and driving long-term success. While project management focuses on individual projects, portfolio management looks at the bigger picture—ensuring that the entire portfolio of projects delivers value to the organization. Planning for portfolio management is not a one-size-fits-all process, but there are core principles you can follow to lay a strong foundation. Let’s dive into a practical approach to planning for effective portfolio management.
Understanding Portfolio Management in Project Settings
Before we start planning, it’s important to understand what portfolio management is in the context of project settings. At its core, portfolio management is about selecting, prioritizing, and managing a collection of projects that align with your organization’s goals. It ensures resources are allocated efficiently and helps in monitoring project performance to maximize returns.
In project-heavy environments, having a portfolio management plan allows you to see the interconnections between projects, identify overlaps, and avoid resource conflicts. The right portfolio management strategy helps minimize risks and ensures that your projects are driving the business forward.
Step 1: Align Projects with Strategic Objectives
Every project in your portfolio should contribute to your organization’s long-term objectives. The first step in planning for portfolio management is to ensure that each project is aligned with these broader goals. Without alignment, even the most successful projects may not deliver the desired business impact.
How to Do It:
- Evaluate strategic priorities: Review your company’s mission, vision, and key business objectives.
- Rank projects: Identify which projects most directly support these objectives.
- Adjust priorities: If there are projects in the pipeline that don’t align, reconsider their place in the portfolio or shelve them entirely.
By ensuring alignment, you’re setting a strong foundation where every project has a purpose and adds value.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
Step 2: Conduct a Resource and Capacity Analysis
A critical aspect of portfolio management planning is understanding your organization’s resources and capacity. Projects will not succeed if resources are stretched too thin, and taking on too many projects can lead to burnout or incomplete work. Conducting a resource and capacity analysis ensures you’re not overcommitting.
How to Do It:
- Inventory resources: Take stock of the team members, tools, budget, and materials you have available.
- Evaluate capacity: Assess the workload each team can handle realistically and avoid overloading them.
- Plan resource allocation: Match available resources with project needs. If resource gaps exist, consider outsourcing or delaying lower-priority projects.
Proper resource management will prevent bottlenecks, ensuring that your projects stay on track and within budget.
Step 3: Develop a Governance Structure
Portfolio management requires a clear governance structure to maintain order and accountability. The governance structure defines who is responsible for making key decisions, monitoring progress, and addressing risks across the portfolio.
How to Do It:
- Define roles and responsibilities: Assign clear roles to ensure accountability. You might appoint a portfolio manager to oversee everything or create a committee for decision-making.
- Establish reporting mechanisms: Set up regular reporting to track project performance and detect any issues early.
- Create decision-making criteria: Outline how decisions will be made about resource allocation, project prioritization, or stopping underperforming projects.
Good governance creates a structured process, helping you stay proactive in managing your portfolio rather than reactive.
Step 4: Prioritize Risk Management
Risk management is critical in any project setting, but even more so when managing a portfolio. With multiple projects running simultaneously, the chances of risks compounding across the portfolio increase. You need a solid plan for identifying and mitigating risks.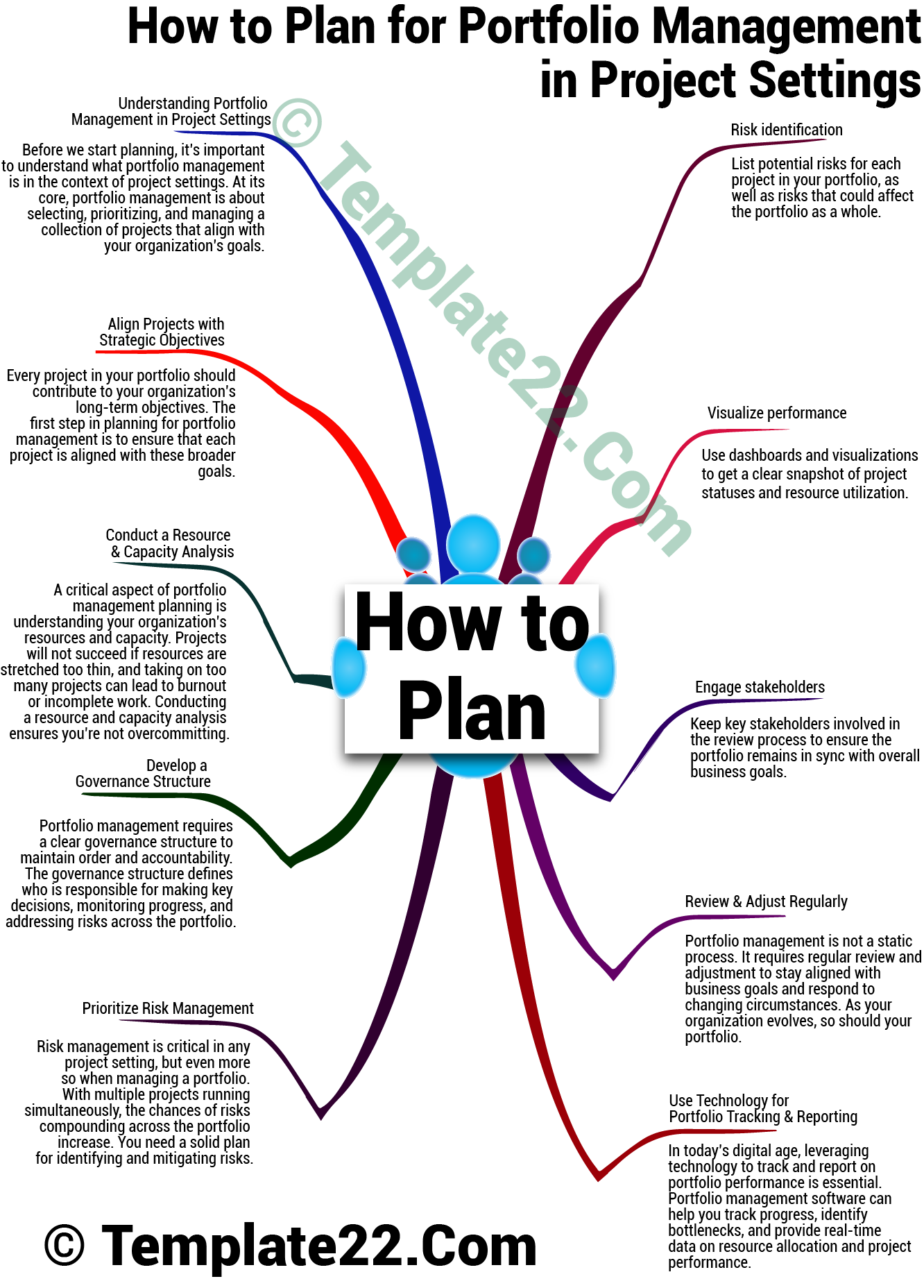
How to Do It:
- Risk identification: List potential risks for each project in your portfolio, as well as risks that could affect the portfolio as a whole.
- Mitigation plans: Develop strategies to minimize risks—whether it’s through contingency planning, insurance, or resource reallocation.
- Continuous monitoring: Regularly review your risk management strategies and adjust as needed to address new risks.
By staying ahead of potential challenges, you can keep your portfolio running smoothly and minimize disruptions.
Step 5: Use Technology for Portfolio Tracking and Reporting
In today’s digital age, leveraging technology to track and report on portfolio performance is essential. Portfolio management software can help you track progress, identify bottlenecks, and provide real-time data on resource allocation and project performance.
How to Do It:
- Select the right tools: Choose a portfolio management tool that integrates with your project management software for seamless tracking.
- Automate reporting: Set up automated reports to keep stakeholders informed without manual effort.
- Visualize performance: Use dashboards and visualizations to get a clear snapshot of project statuses and resource utilization.
Using technology helps streamline your portfolio management efforts and ensures you can make data-driven decisions.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
Step 6: Review and Adjust Regularly
Portfolio management is not a static process. It requires regular review and adjustment to stay aligned with business goals and respond to changing circumstances. As your organization evolves, so should your portfolio.
How to Do It:
- Schedule regular reviews: Periodically assess your portfolio’s performance and alignment with strategic objectives.
- Be flexible: Be open to shifting priorities or stopping projects that are no longer delivering value.
- Engage stakeholders: Keep key stakeholders involved in the review process to ensure the portfolio remains in sync with overall business goals.
This regular review cycle ensures that your portfolio remains agile and adaptable to changing market conditions or internal shifts.
Conclusion
Planning for portfolio management in project settings is essential for any organization aiming to maximize value across multiple projects. By aligning projects with strategic objectives, managing resources effectively, establishing governance, and using technology, you can create a robust portfolio management plan. Regular reviews and adjustments will ensure that your portfolio remains optimized and contributes to long-term success.
Effective portfolio management isn’t about micromanaging every project; it’s about seeing the big picture and making smart decisions that lead to sustainable growth.
