 Every project comes with its share of risks. Identifying and managing these risks early—especially during the planning phase—can significantly increase your chances of success. Without a proactive approach, risks can derail even the most promising projects, leading to delays, cost overruns, and, in the worst cases, complete failure. So, how do you ensure that you’re on top of these potential issues? Let’s explore how to effectively identify and Managing Project Risks during the planning phase.
Every project comes with its share of risks. Identifying and managing these risks early—especially during the planning phase—can significantly increase your chances of success. Without a proactive approach, risks can derail even the most promising projects, leading to delays, cost overruns, and, in the worst cases, complete failure. So, how do you ensure that you’re on top of these potential issues? Let’s explore how to effectively identify and Managing Project Risks during the planning phase.
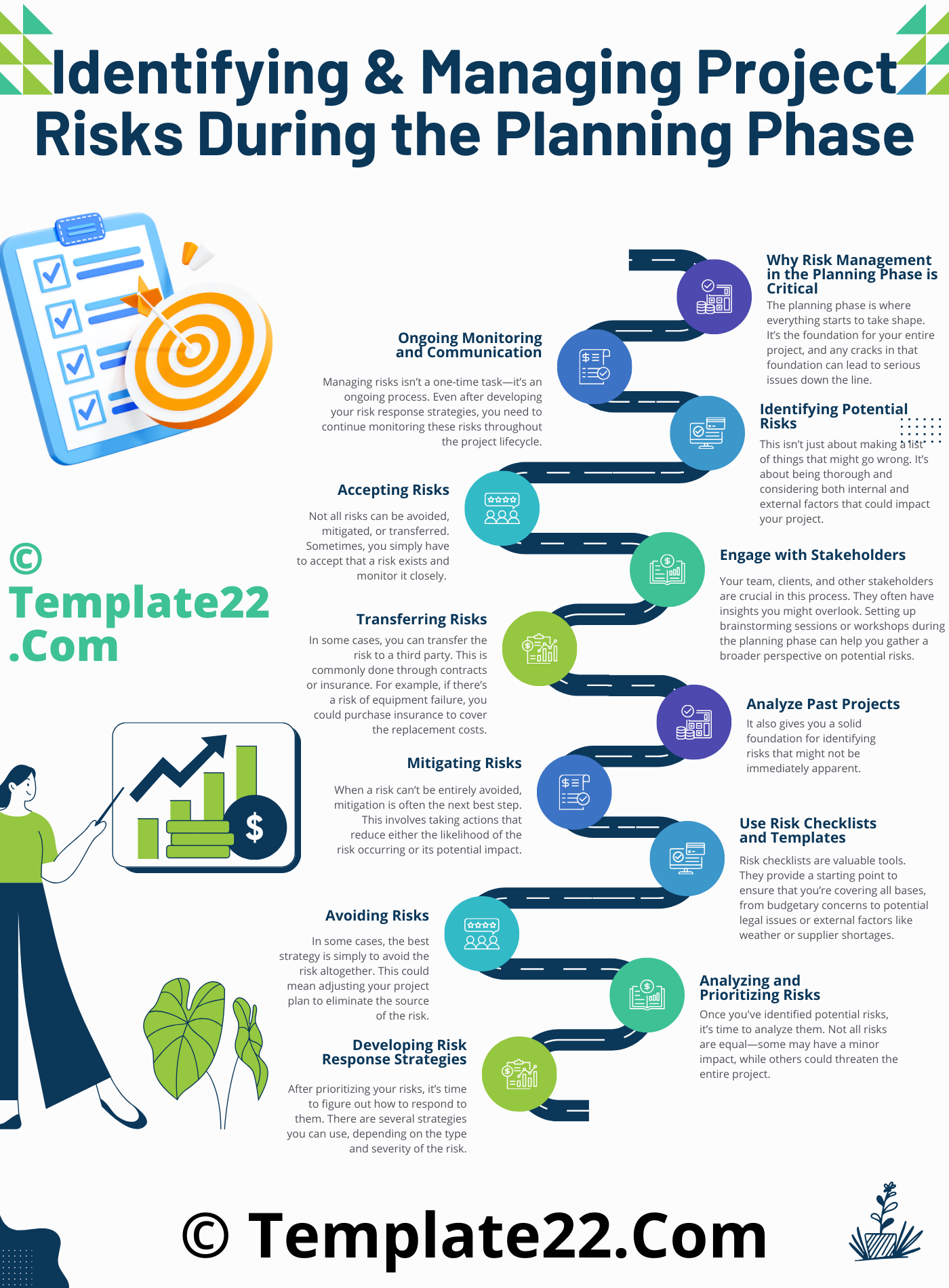
Why Risk Management in the Planning Phase is Critical
The planning phase is where everything starts to take shape. It’s the foundation for your entire project, and any cracks in that foundation can lead to serious issues down the line. Identifying risks early allows for smoother execution and a more predictable project journey. It’s much easier (and cheaper) to address potential problems before they happen rather than scrambling to fix them when the project is already underway.
Effective risk management during planning helps ensure:
- A more realistic timeline
- Better resource allocation
- Increased stakeholder confidence
- A higher likelihood of meeting your project goals
Step 1: Identifying Potential Risks
The first step in managing project risks is to identify them. This isn’t just about making a list of things that might go wrong. It’s about being thorough and considering both internal and external factors that could impact your project.
Engage with Stakeholders
Your team, clients, and other stakeholders are crucial in this process. They often have insights you might overlook. Setting up brainstorming sessions or workshops during the planning phase can help you gather a broader perspective on potential risks.
Analyze Past Projects
Look back at previous projects. What risks did they face? Were there budget issues? Delays? Resource shortages? Learning from history is one of the best ways to avoid repeating mistakes. It also gives you a solid foundation for identifying risks that might not be immediately apparent.
Use Risk Checklists and Templates
Risk checklists are valuable tools. They provide a starting point to ensure that you’re covering all bases, from budgetary concerns to potential legal issues or external factors like weather or supplier shortages. Templates can help standardize your risk identification process, ensuring consistency across different projects.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
Step 2: Analyzing and Prioritizing Risks
Once you’ve identified potential risks, it’s time to analyze them. Not all risks are equal—some may have a minor impact, while others could threaten the entire project. Therefore, prioritizing them is key to effective management.
Assess the Impact and Probability
For each risk, evaluate two things:
- Impact: How severe would the consequence be if this risk materialized?
- Probability: How likely is it that this risk will happen?
This analysis helps you rank risks, allowing you to focus on the ones that pose the greatest threat to your project. Some teams use a risk matrix—a simple grid that helps visualize the probability and impact of each risk. High-probability, high-impact risks should be dealt with immediately, while low-probability, low-impact risks might simply be monitored.
Step 3: Developing Risk Response Strategies
After prioritizing your risks, it’s time to figure out how to respond to them. There are several strategies you can use, depending on the type and severity of the risk.
Avoiding Risks
In some cases, the best strategy is simply to avoid the risk altogether. This could mean adjusting your project plan to eliminate the source of the risk. For example, if you’re worried about delays due to weather conditions, you might shift your timeline or choose a different location.
Mitigating Risks
When a risk can’t be entirely avoided, mitigation is often the next best step. This involves taking actions that reduce either the likelihood of the risk occurring or its potential impact. If your risk involves budget overruns, for instance, you might build contingencies into your budget.
Transferring Risks
In some cases, you can transfer the risk to a third party. This is commonly done through contracts or insurance. For example, if there’s a risk of equipment failure, you could purchase insurance to cover the replacement costs.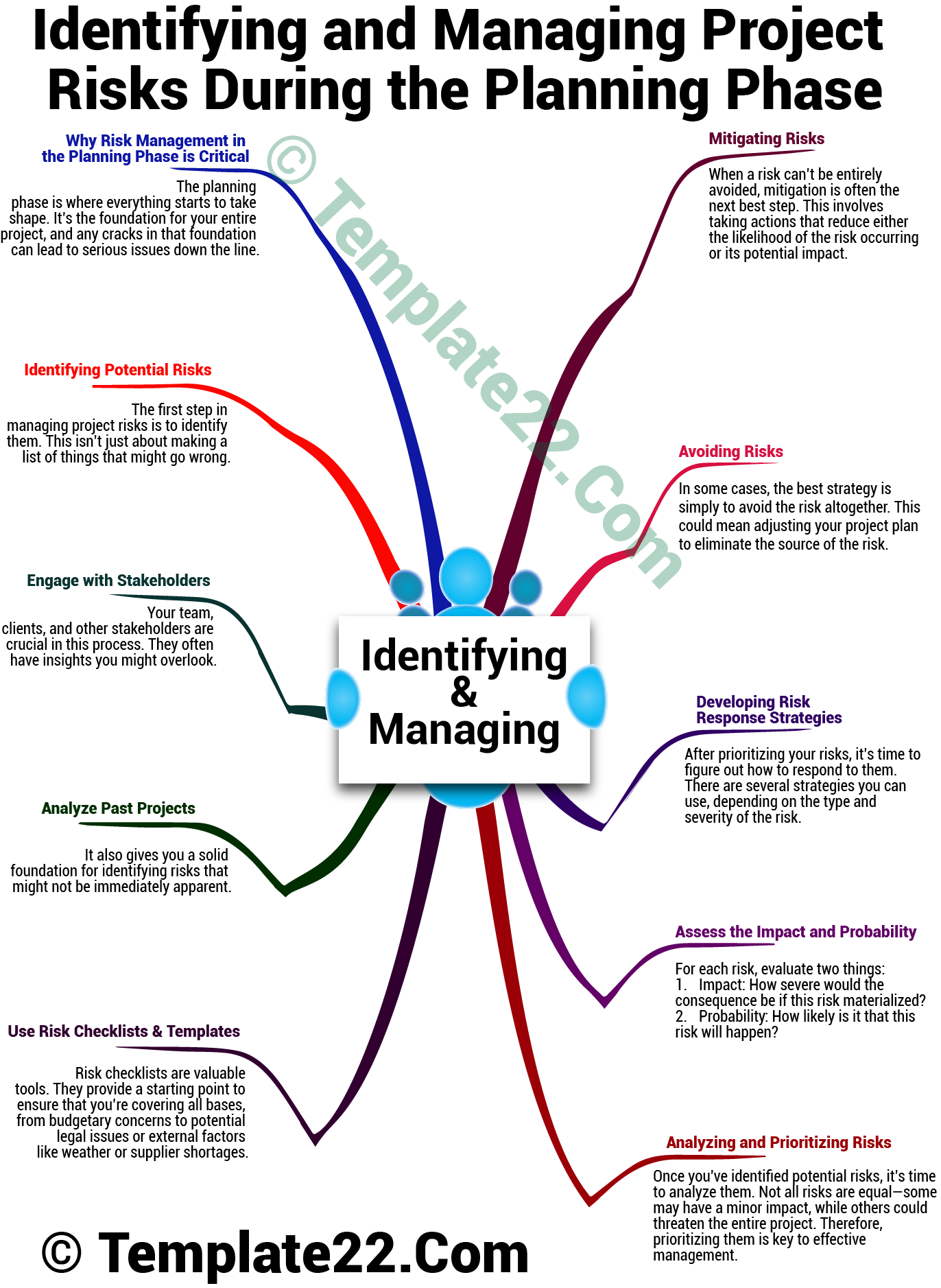
Accepting Risks
Not all risks can be avoided, mitigated, or transferred. Sometimes, you simply have to accept that a risk exists and monitor it closely. If it’s a low-impact, low-probability risk, it may not be worth spending time and resources to manage it beyond basic monitoring.
Step 4: Ongoing Monitoring and Communication
Managing risks isn’t a one-time task—it’s an ongoing process. Even after developing your risk response strategies, you need to continue monitoring these risks throughout the project lifecycle. Regular check-ins, updates to your risk register, and open lines of communication with your team and stakeholders ensure that any new risks are identified and managed quickly.
Use Tools for Tracking
Various project management tools help with risk tracking, allowing you to update risk statuses, assign responsibility, and maintain visibility on how risks are evolving. Tools like Trello, Asana, or more comprehensive platforms like Microsoft Project can make this process smoother.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
Keep Stakeholders Informed
Clear communication is key. Keep your stakeholders updated on any risks and how you plan to address them. Regular reporting ensures everyone is aligned and can react quickly if risks materialize.
Conclusion: A Proactive Approach to Risk Management
Identifying and managing project risks during the planning phase is essential to ensuring smooth project execution. By taking a proactive approach—engaging stakeholders, analyzing past projects, and using structured tools and strategies—you can mitigate the majority of risks before they have a chance to disrupt your project. Remember, risk management isn’t just a checkbox. It’s an ongoing, integral part of successful project planning that helps deliver results on time, within budget, and to specification.
