 A well-structured project plan is essential when managing a project. Think of it as your project’s roadmap, laying out the route from concept to completion. But what does a project plan include, and why is its structure so important? Let’s explore each component of an effective project plan, breaking down its structure in a way that helps ensure project success.
A well-structured project plan is essential when managing a project. Think of it as your project’s roadmap, laying out the route from concept to completion. But what does a project plan include, and why is its structure so important? Let’s explore each component of an effective project plan, breaking down its structure in a way that helps ensure project success.
What is a Project Plan?
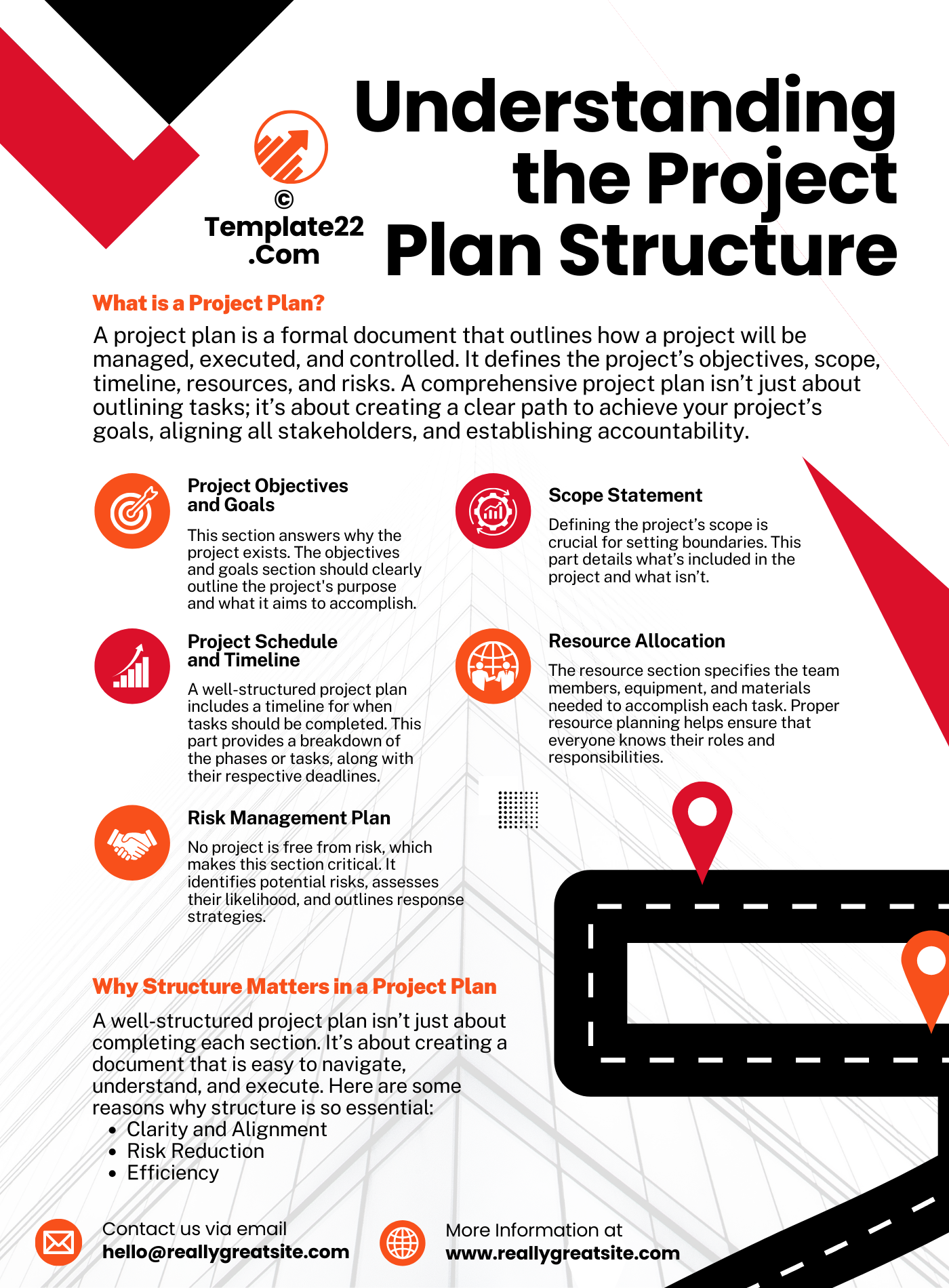
A project plan is a formal document that outlines how a project will be managed, executed, and controlled. It defines the project’s objectives, scope, timeline, resources, and risks. A comprehensive project plan isn’t just about outlining tasks; it’s about creating a clear path to achieve your project’s goals, aligning all stakeholders, and establishing accountability.
Key Elements of a Project Plan Structure
A project plan generally consists of several key components. Let’s review each section to see what’s included and why it matters.
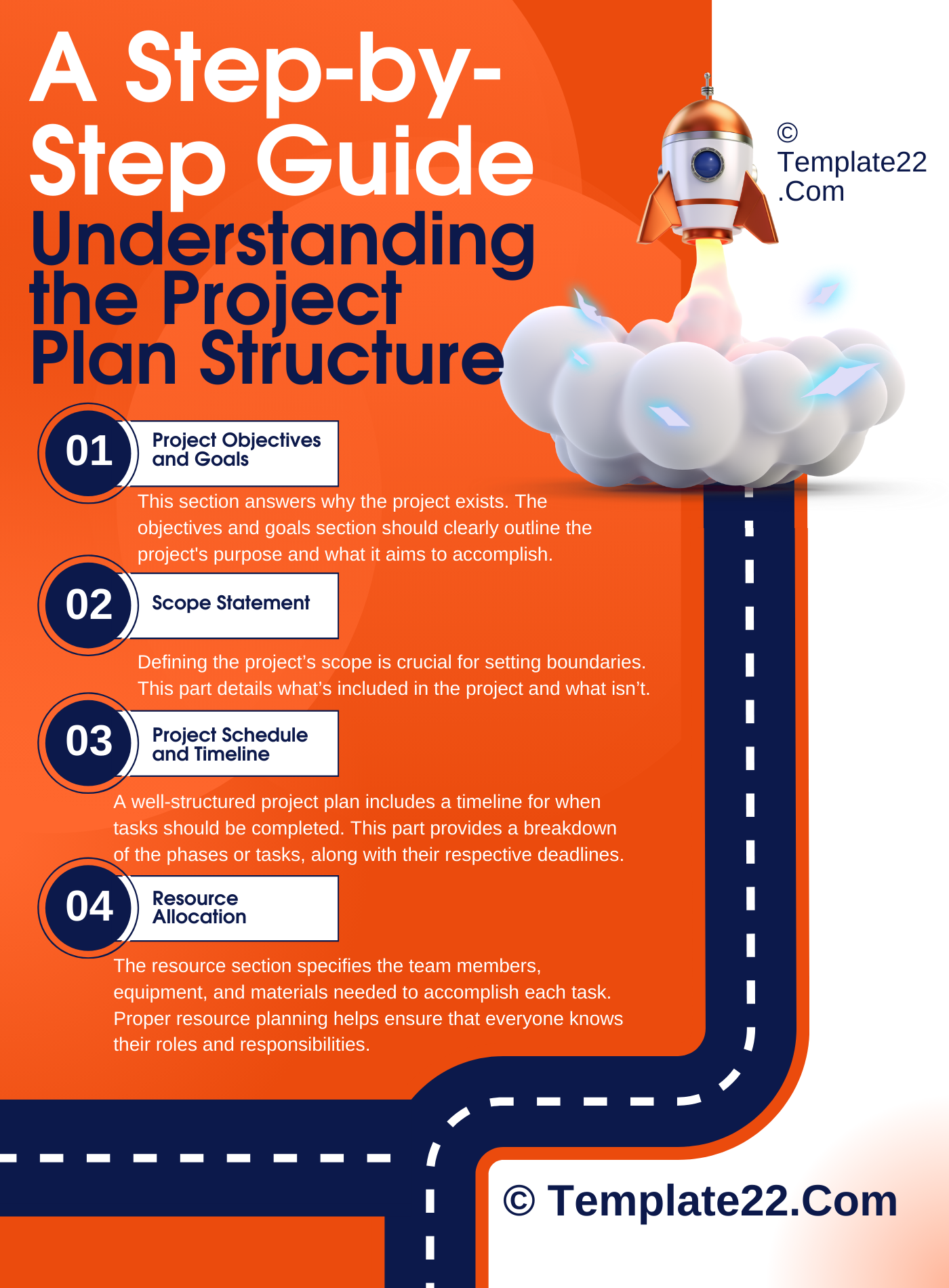
1. Project Objectives and Goals
This section answers why the project exists. The objectives and goals section should clearly outline the project’s purpose and what it aims to accomplish. Are you trying to increase customer satisfaction? Improve team efficiency? This section provides clarity and motivation for everyone involved.
- Project Objectives: Specify the project’s purpose and its desired outcomes.
- Goals: These are measurable milestones you hope to achieve during the project. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
2. Scope Statement
Defining the project’s scope is crucial for setting boundaries. This part details what’s included in the project and what isn’t. By outlining the project’s limitations, you can avoid scope creep, which is when projects expand beyond their original goals.
- Inclusions: Describe the deliverables and objectives.
- Exclusions: List what’s outside the project’s focus.
- Acceptance Criteria: Define standards for each deliverable to be considered complete.
3. Project Schedule and Timeline
A well-structured project plan includes a timeline for when tasks should be completed. This part provides a breakdown of the phases or tasks, along with their respective deadlines. It’s best to use a Gantt chart or timeline view to visualize the schedule.
- Milestones: Identify major checkpoints within the project.
- Deadlines: Set specific dates for each task or phase.
- Dependencies: Note tasks that depend on the completion of others.
4. Resource Allocation
The resource section specifies the team members, equipment, and materials needed to accomplish each task. Proper resource planning helps ensure that everyone knows their roles and responsibilities.
- Human Resources: Outline who will work on each task.
- Budget: Estimate costs for resources, materials, and contingency.
- Tools and Equipment: Specify tools required for various stages.
5. Risk Management Plan
No project is free from risk, which makes this section critical. It identifies potential risks, assesses their likelihood, and outlines response strategies.
- Risk Identification: List potential issues that could impact the project.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate each risk’s likelihood and impact.
- Mitigation Strategies: Develop action plans to address each risk.
6. Communication Plan
Clear communication is essential for keeping stakeholders informed and aligned. This section defines how information will be shared, when, and with whom.
- Stakeholder Matrix: Identify all stakeholders involved.
- Communication Methods: Define channels like emails, meetings, and reports.
- Frequency and Responsibility: Specify how often updates will be provided and who is responsible.
Why Structure Matters in a Project Plan
A well-structured project plan isn’t just about completing each section. It’s about creating a document that is easy to navigate, understand, and execute. Here are some reasons why structure is so essential:
- Clarity and Alignment: When everything is laid out, team members have a shared understanding of the project’s objectives, roles, and timelines.
- Risk Reduction: With a structured plan, you’re better prepared to foresee potential risks and proactively address them.
- Efficiency: A structured approach streamlines workflow by eliminating ambiguity, allowing tasks to be completed efficiently and on time.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD 300+ PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEMPLATES & DOCUMENTS IN EXCEL
Tips for Creating an Effective Project Plan
Now that we’ve broken down the key sections, here are a few tips to make your project plan as effective as possible:
- Keep It Simple: Don’t overwhelm stakeholders with unnecessary details. Focus on clarity and brevity.
- Update Regularly: Projects evolve, so keep your plan current to reflect any changes in scope, timeline, or resources.
- Use Project Management Software: Tools like Microsoft Project, Asana, or Trello can help organize your plan, track progress, and improve collaboration.
Conclusion
Understanding the structure of a project plan is crucial for any project manager. By organizing your plan into clear sections—objectives, scope, schedule, resources, risk management, and communication—you set a solid foundation for project success. With a well-structured project plan, you’re not just planning for a successful outcome; you’re creating a roadmap that guides your team, aligns stakeholders, and minimizes risks.